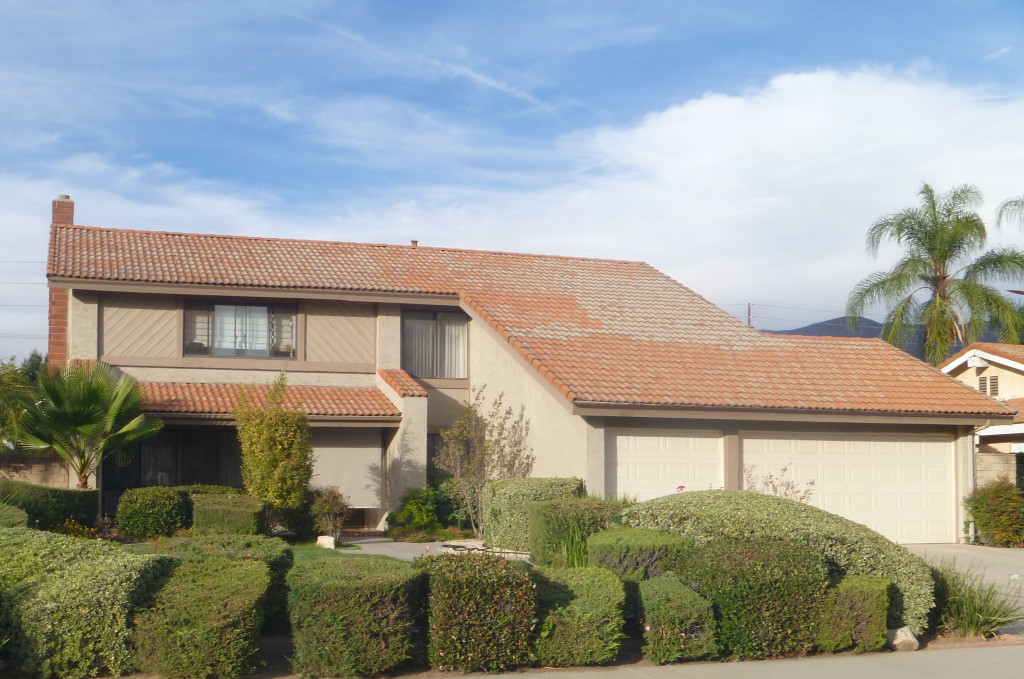
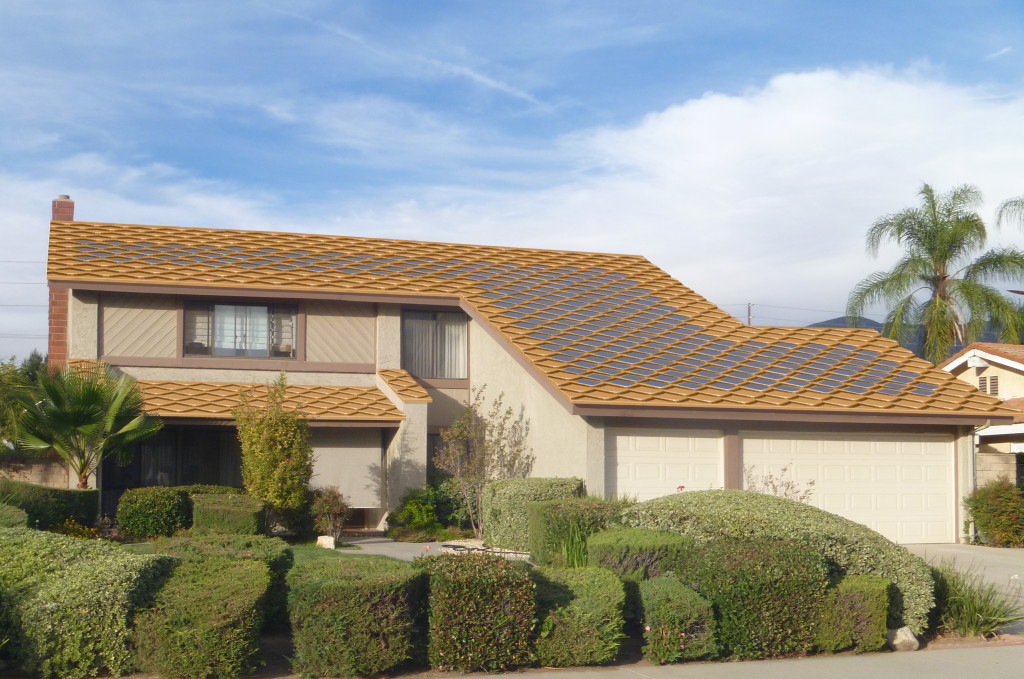
Components of building resilience (the four R’s) from the National Institute of Building Sciences [1] are described below with examples applicable to an energy efficient solar roof:
Robustness. The ability to maintain critical operations and functions in the face of crisis. Roof temperature moderation with an energy efficient roof allows a smaller HVAC system design, and also a smaller solar and battery system design. Having solar power with possible electrical energy storage allows backup in power outage conditions. The smaller systems allow construction budgets room to afford other building features. Lightweight tiles, such as the Power Shield Inc. (PSI) metal tiles present less potential stress on a building during an earthquake. The metal tiles are fireproof.
Resourcefulness. The ability to skillfully prepare for, respond to and manage a crisis or disruption as it unfolds. This includes identifying courses of action and planning business continuity; training; supply chain management; prioritizing actions to control and mitigate damage; and effectively communicating decisions. For safety reasons, utility companies don’t want solar systems to be able to feed power into the grid when utility workers may be working on the lines—so there are safeguards to prevent that. In most cases, this means that when the grid goes down, the homeowner can’t draw power from the solar system even during the day in sunlight (anti-islanding). Some inverters allow the use of one AC circuit (with a hard disconnect from the grid during a power outage) to be supplied with power. Battery backup systems like the Enphase Energy AC or the Tesla Powerwall can be configured to draw power from a solar array without risk that power will be back-fed into the grid.
Rapid recovery. The ability to return to and/or reconstitute normal operations as quickly and efficiently as possible after a disruption. Components of rapid recovery include implementing carefully drafted contingency plans, with people and resources toward the right places. Matching priority equipment with the available solar and/or backup power is important. Recovery will be faster for a building with the PSI system, which does not heat up as much as a building with typical roofing.
Redundancy. This means there are back-up resources to support the originals. Typically for homes, this means a battery back-up or a portable generator. There can be connection with equipment such as lights, food refrigeration and fans to operate in back-up modes. Redundancy design options are at the lowest cost when a building is built. Control systems can be intelligent enough to take account of available resources, such as solar power, battery availability and potential modes of operation to respond automatically and to allow building supervisor(s) to modify this response based upon available information on the length of the power outage.
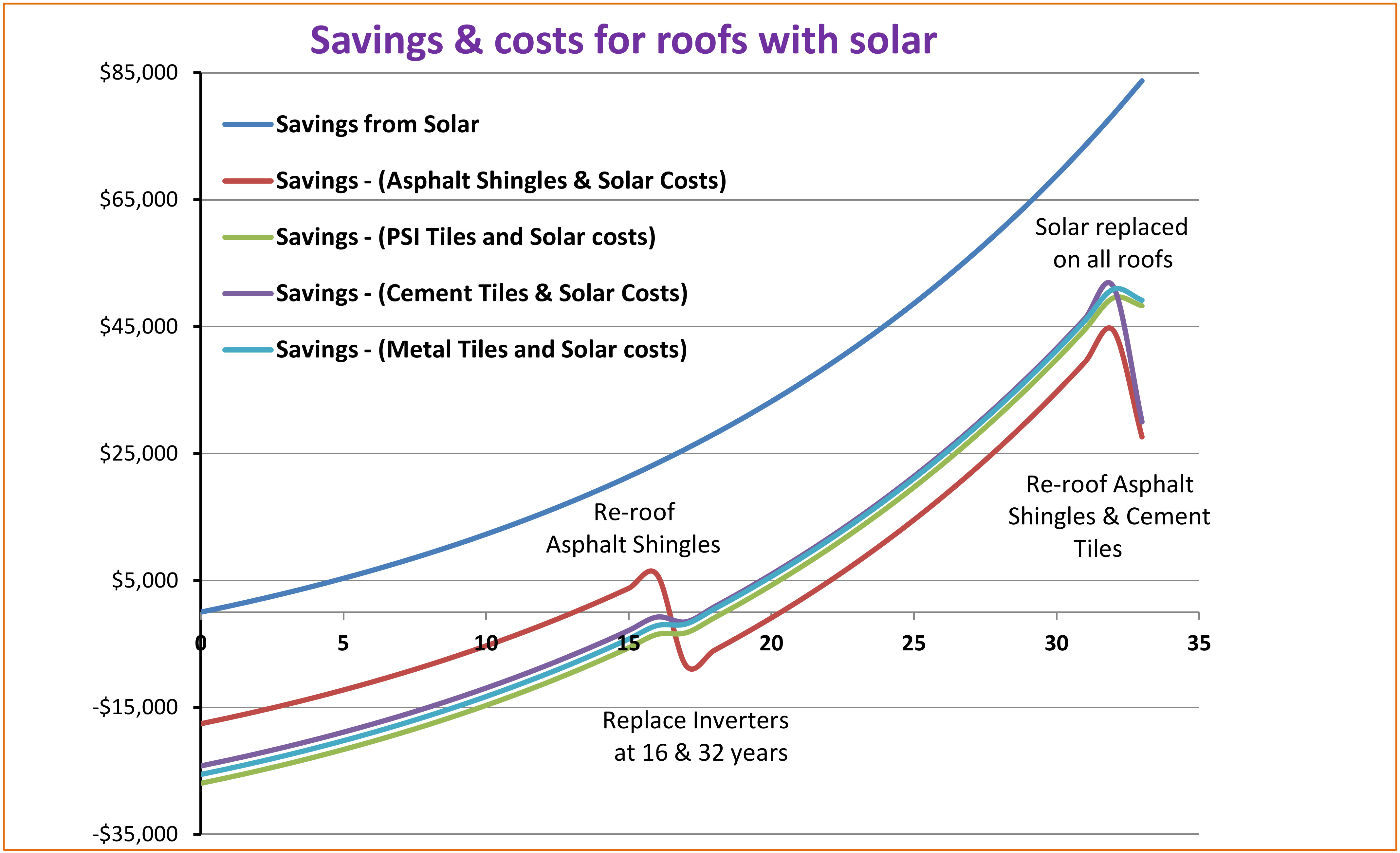
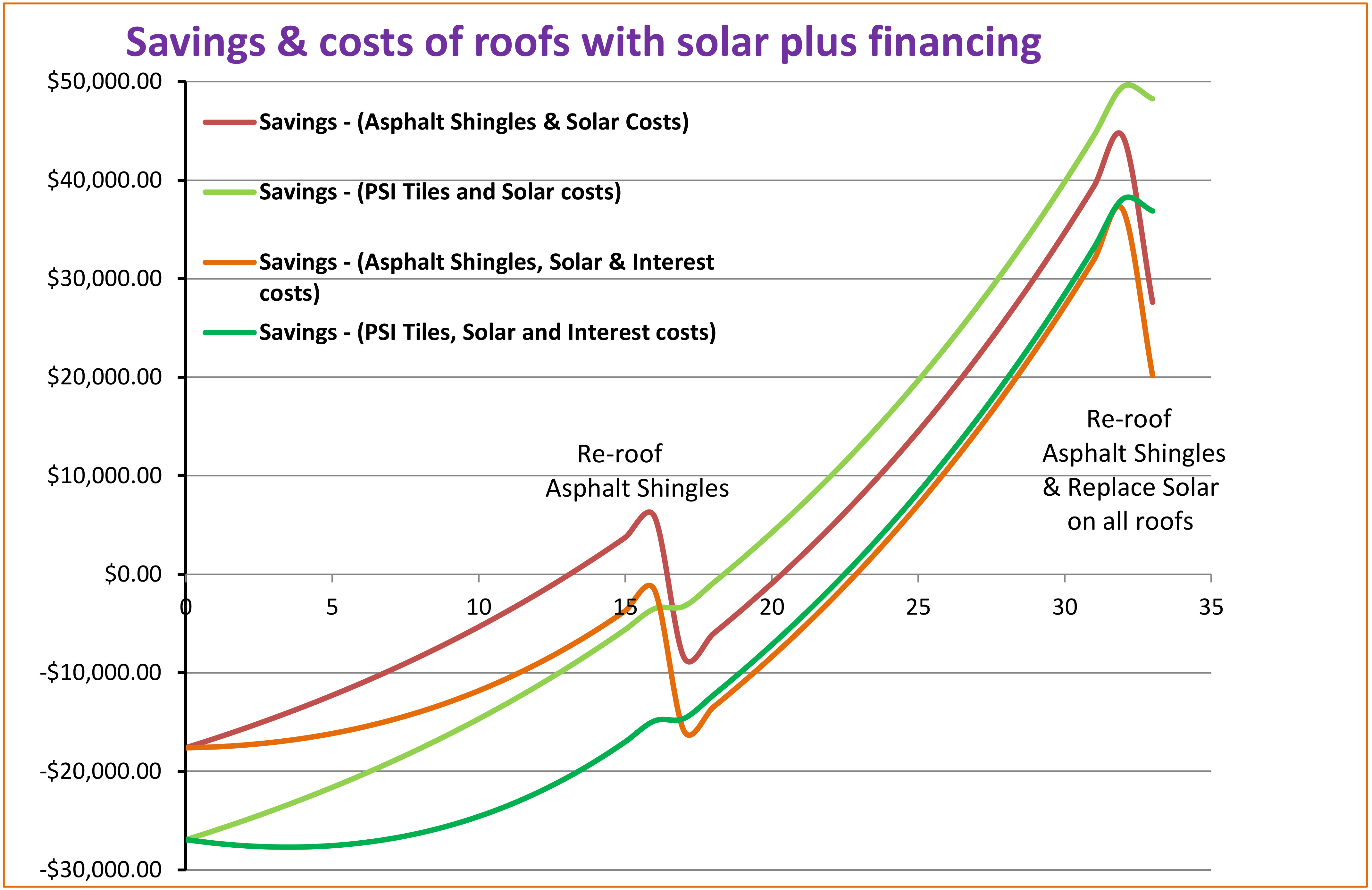
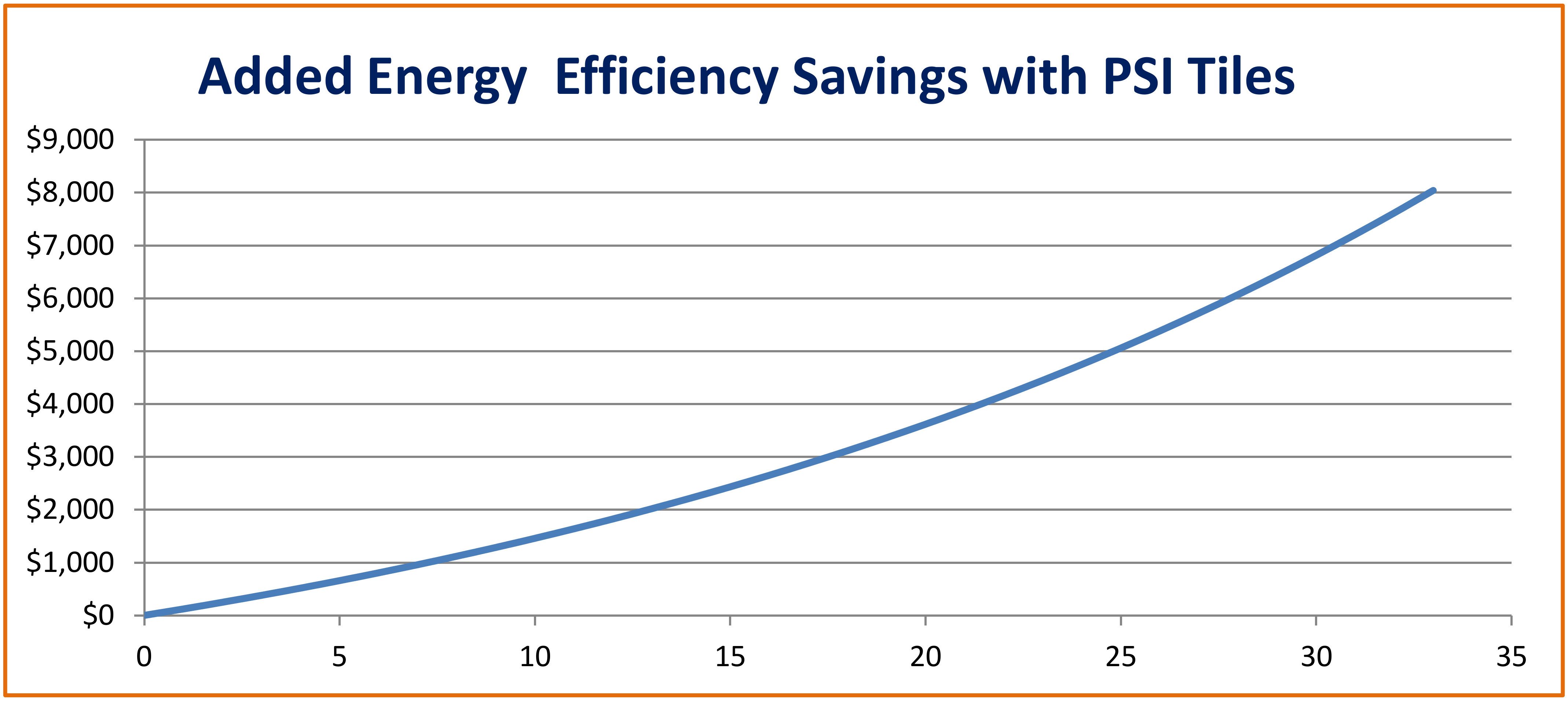
Oak Ridge National Laboratory has performed tests on similar tile configurations as the PSI system and demonstrated that a cool roof coating on metal roof tiles with above sheath ventilation (ASV) are effective means to reduce heat transfer from the roof to the building interior [2]. As much as 30% of the cooling energy can be achieved with these measures. These studies are for steep slope roofing applicable to residential and commercial buildings. For power outages or brownouts during the cooling season, occupant area temperatures and comfort can be improved through a cooler roof with low heat transfer. Air conditioning is typically not a high priority system during power outages because it can take approximately up to half of the building electrical demand and usage. ASV can minimize the heat loss of cool roof coatings during heating season, because of the insulating gap between the tiles and roof deck. It can help in preventing ice dams in conditions prone to them. Blackout and brownout scenarios can be random, for planned maintenance or happen because of programmed outages in fire hazard areas, such as California, where large area blackouts occur because of location, winds and dry conditions. A metal roof tile system is naturally fire resistant and will work well in wildland urban (WUI) interface zones.
An energy efficient roof with solar are often of high priority for authorities having jurisdiction (AHJ) and building efficiency organizations, such as ASHRAE, DOE, ICC, NFPA and others.
[1] https://www.wbdg.org/resources/building-resiliency
[2] A Compilation of Home Energy Assessments for Cool Roofs, Above-Sheathing Ventilation, Radiant Barriers, and Other Attic Strategies William Miller, PhD. ASHRAE 2010 Buildings XI.